
Several media articles have claimed that Artificial Intelligence technology will end human life and that technological singularity is just around the corner. Headlines like these generate huge backlash because ordinary people cannot comprehend where this revolutionary technology is taking us. Technology innovations considered to drive economic growth worldwide lack a practical evaluation tool.
There is a temptation to present technology in the best possible light to attract investors, secure funding, or gain public attention. Researchers and entrepreneurs might be genuinely enthusiastic about the possibilities but may not correctly grasp the challenges or potential negative consequences.
We can sometimes be far ahead of the technology curve by introducing revolutionary things as they are already here. To effectively sell the breakthrough concept, the entrepreneur typically shows a real-life example of their innovation during their presentation. Despite that, it is not particularly apparent that this is a fabricated showcase, manipulated photography, a theoretical example, or a prearranged setup to illustrate how it might look. As a result, people are often confused since they believe they have seen the new innovation in action. Among these examples are self-driving cars, robots walking and acting and talking like humans, holograms and the metaverse, and so on. One must be patient. Many technological innovations are still speculations, ideas, or theories; therefore, it is unknown when or if they will become a reality. However, the entrepreneurs do not doubt that their concept or theory will become a reality; instead, it is just a matter of time and financing.
Based on these speculations, we frequently hear irresponsible statements like “doomsday is coming soon” or “robots will take over your job,” recklessly proclaimed by high-profile figures. Some people have expressed fears that technological singularity is coming and that Artificial Intelligence technology will replace humans altogether. There is no concrete evidence that it will happen; it is merely speculative.
A more practical approach to moving forward is to view human intelligence and technology innovation as know-how amplifying human potency, where each entity brings its skills, knowledge, and strength to the table.
Consumer Insights Drive All Changes
The world’s most significant innovations are often developed over a long time before becoming a reality. In that case, the latest ideas and theories on the matter are spread among people at the outset. Prototypes are developed and introduced as part of the innovation process, and at the final development stages, things spark off.
Acquiring capital is the most challenging phase of making an invention a reality. During this process, a mechanism is put in place to understand the business opportunity of the invention. It will be a success if innovation is conceived to capture, create and fulfill evolving consumer needs on a dynamic scale. By evaluating consumer insights, emerging needs and trends can be identified. A deep understanding of consumer insights is the foundation for discovering the most relevant business opportunities that drive competitive advantages. Consumer insight information can open up new sales opportunities through “ah-ha” discoveries. Discoveries are crucial for making accurate investment decisions and launching and introducing relevant brand products and services.
By understanding the user’s behavior and needs, entrepreneurs can create new sales opportunities that capture and create more demand, effectively fulfilling the target group’s needs. If an obvious need exists, the opportunity can be taken advantage of without hesitation, and the product can be released to the next phase without delay.
It is crucial to identify the “critical one” that is both differentiating and relevant, as well as the size that makes it rational to capitalize on the latest brand and service improvements. Entrepreneurs need to know who their potential target consumers are. What do they do? Who buys? What and when do they buy? Why do they buy, and what do they like and dislike about the technology innovation products?
Consumer insight means understanding each touch point the consumer or user has with a brand. The “ah-ha” discoveries can best be captured through a systematic consumer insight analysis, focusing on the offer’s perceived value. Consumer understanding sparks investor interest in participating in the innovation process, making it possible to become a reality.
The Strategic Model of Technology Innovation
Over the past few years, we have been introduced to several complicated technological disruptions. We observe a variety of inventions, advancing methods, practices, and processes, and completely different ways of doing something differently. All areas of daily life are affected by revolutionary technology. Many technological innovations have caused job redundancies on a large scale, and the situation seems to be accelerating.
Moreover, business leaders tend to explain technological innovation as a solitary thing, all within the same Internet business. The common subjects include eCommerce, Big Data, the Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, quantum computing, and digital business, to name a few. One must understand that technology innovation crosses all industries and affects employees, homes, and families. Everything is changing. People’s regular day-to-day routine has significantly changed. People’s stress levels, uncertainties, and impulsiveness have accelerated to new heights. Businesses are viciously attacked, forcing them to take immediate action if they are to survive. For companies, maintaining the status quo means losing revenue and profit, ultimately leading to bankruptcy.
Technology transformation is a multifaceted process. It isn’t easy to understand how everything connects with everything else. Moreover, for technology innovation to succeed, many technologies must be integrated into one unified whole. As a result, it isn’t easy to understand where technological innovation will lead us in the future.
It is imperative to understand how everything connects with everything else. New technology innovation’s negative implications over the short term do not necessarily represent their long-term effects. For example, technological innovations will likely create various supplementary jobs over the long term. This has happened in the past radical innovation periods. The primary vision of technology innovation is clear, and that is to make remarkable things happen to make a better world.
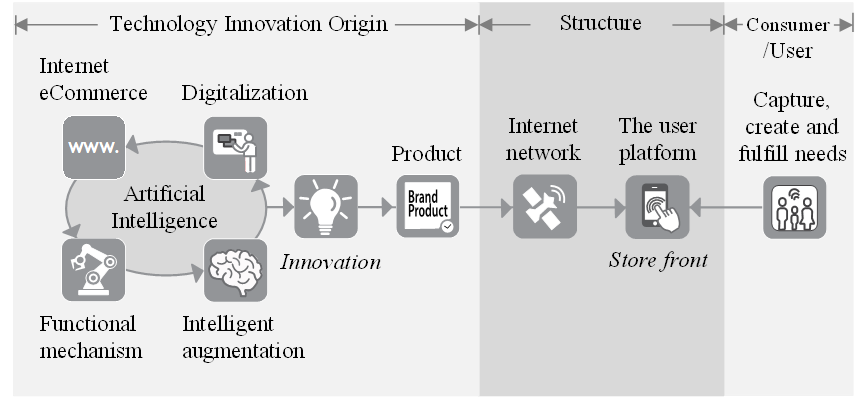
So far, the Strategic Model of Technology Innovation has not been systematically identified and structured. Through the model, we can learn about and test the leading technological innovations, their business models and structures, their routes to market, and how they make revenue and profit.
Structuring technology innovation helps us understand where we are at and where we are heading with all these complex marriages of technologies. Additionally, it is essential to understand how the infrastructure is utilized to transfer the product and service to consumers and end-users.
Let us briefly explain the Strategic Model of Technology Innovation figure above, starting with the consumer and end-users.
Consumers and/or end-users:
The first question is always; will the consumer need it and want it? Unfortunately, many of today’s inventions lack understanding and the capability of capturing, creating, and fulfilling consumer needs. Are consumers likely to appreciate autonomous vehicles, for example? What about flying cars? What is the size scale? It is also critical to understand the system’s economics before proceeding with firm execution.
- Consumer and or end-user information is the driver for all changes. Ultimately, consumer acceptance determines whether the new invention will be a success or not. Furthermore, the scale at which an opportunity arises determines its opportunity.
The structure:
The structure is where the rubber meets the road. This is where the users interact with the products and services themselves. This is the place where consumers and end-users get in direct contact with the end product, its selling point, user experiences, Internet speed, Web design, and so on. Positive consumer experiences using the Website drive a successful business. Structural design and user experience must be flawless from the first click to payment, delivery, and after-sales services. You do not have a second chance; flawed platform design drives poor user experiences. When users interact with the brand’s products and services, platform design and Internet speed determine how engaging the occasion is.
The structure is composed of the following two elements:
- A user platform is where users interact with an offer and decide whether to purchase a product or service. A platform connects a brand and its service offering with the user. It is essentially a storefront that displays text content, photos, and product offerings. When a user visits an online site, the platform represents the “aesthetics” of the site. It is also the basic concept in terms of developing and putting together all the “technical platforms” through which a user interacts when visiting an online site. The user platform is designed to drive sales success and the perception of brand and service values.
- The Internet network allows computer users to connect with other computers through text, voice, visuals, and much more. The Internet network is a global electronic communications network that enables computers to exchange data with each other. It is open for everyone to access and use. The network connects the entire world through a global communication network. The Internet’s “last mile” is the connection that generates the most significant barrier to speed. Slow speeds turn users off, which can be a barrier to growth. Thus, Internet speed is becoming among the highest priorities for Internet users and Web companies.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI is computer software that mimics the function of the human brain. The human brain has put the world where it is today. Therefore, one of the best-known blueprints for the next generation of computer systems is to emulate the brain’s structure and functions. In that case, AI is the principal algorithm that marries different technologies to create a unified and flawless product. Generally, the most radical technological advances are supported by AI algorithms. However, the design is supported by traditional analog and digital algorithms, using a binary numbering system consisting of ones and zeros.
- Artificial Intelligence is the science of bringing value to humankind by making machines smart. It involves utilizing digital opportunities, exploiting intelligent augmentation, and creating virtual reality, among others. AI is a science that enables algorithms to learn and improve themselves in terms of uncovering innovative and effective ways of doing things. Artificial Intelligence algorithms can basically teach themselves to learn and improve upon themselves. This is often without the programmer knowing, at later stages, the reason why and how the machine came to a particular conclusion.
Technology innovation origin:
Technology Innovation’s origins have been divided into four product categories. Its technological makeup and its product role determine its category. Even though multiple technology innovations require marrying several technologies to meet their purpose, the end product determines its category. Categorizing technology products into groups generates better understanding, as products naturally have similar technological backgrounds. Even so, the technology developed for the brand’s products could eventually be applied to another category at later stages. In some instances, the sub-products might be assigned to two technology categories, and then it might be revealed that the product is assigned to dual product categories.
Technology innovation sources have been defined and broken down into four possible categories as follows:
- eCommerce is buying or selling products and services, including payment transfers, over the Internet network. This is the business model where companies sell their brand products and services directly to consumers and customers. Thus, of the four technology categories, this is the largest category in terms of revenue. The eCommerce business model has disrupted many traditional businesses, forcing them to change fast if they are to stay in business in the future. eCommerce has radically changed the world and continues to do so. This category also includes social networks (such as social media, search engines, and online newspapers) and financial services.
- Digitalization utilizes digital technology to transform a business model, sales and service process, and operational process to build competitive advantages through streamlining. For example, regulatory functions such as taxes, laws, and customs are increasingly becoming digitalized by connecting people with things and things with things to increase efficiencies. Moreover, this is to improve services at the lowest possible cost.
- Functional mechanisms are self-learning machines and robots that exploit smart sensors, devices, and wireless networks, helping machines learn by themselves and discover by doing. Moreover, through augmented reality and digital readings, robots and machines can make accurate diagnoses and acquire knowledge.
- Intelligent augmentation focuses on innovations in providing better health and medicine, a longer life expectancy, improved education, and intelligence and knowledge. The intelligent augmentation category is the most aspirational in expectations and holds the most significant potential to make a better world for everyone. This group comprises algorithm and software development, quantum computing development, augmented and virtual reality, cyber security, healthcare, biology, medical science, renewable energy, outer space science, and educational evolution.
Many radical innovations are in progress as we stand at a fantastic time in human history. This is because we live in an age of technological innovation. The status quo is not an option. It is engraved into people’s DNA to constantly invent something new to make a better life for everyone. We are at the very beginning of the technology innovation age.
The key to this transformation process is not to forget that technology innovation is almost always business-oriented. It is basically all about business, market share, revenue, and profit.
It is all About Business!
Let us use the Strategic Model of Technology Innovation to understand how emerging technology will generate revenue and profit in the future. A radical Technology Innovation can be valued accurately with this approach. The question is, how big is it? Will it be the next big business? We will discuss two Technology Innovation examples, autonomous vehicles, and generative AI, as follows:
A) Autonomous vehicles
In our “Strategic Model of Technology Innovation,” autonomous driving falls under the “functional mechanism” category. Autonomous vehicles have three spectrums of consumer usage and needs and can generate revenue and profit as follows:
- Private passenger vehicle: privately owned vehicle transporting people from A to B. This also includes taxis, Ubers, and car rental vehicles. Autonomous vehicle technology will be sold as an optional feature with an all-new vehicle purchase. The seller provides free software updates similar to navigation systems in modern vehicles. The vehicle owner will be responsible for vehicle safety. The companies are working hard to find ways to increase their revenue through subscriptions to their services.
- The last mile delivery vehicle: Direct store delivery (DSD), customer delivery, and home delivery is defined as delivery from the supplier, wholesaler, third party, or Web stores directly to retail stores, customer outlets, or home addresses. Delivery services to customers and outlets are the most challenging for autonomous vehicles. Without a driver, packages cannot be delivered from the vehicle to the customer’s doorstep. For last-mile deliveries, the driver’s role is twofold. Firstly, driving the delivery vehicle, and secondly, delivering the right products to the right customer outlet (home address or a building). Thus delivering to the customer’s door will be difficult without a human driver. Autonomous vehicles could be possible if package delivery solutions were found. It will be costly and challenging to manage this process at later stages.
- Transport to central warehouses: This is transport from production sites to central warehouses and/or transport between central warehouses commonly carried out in full container loads (FCL). Warehouse-to-warehouse transportation is considered the most significant opportunity for autonomous vehicles. This is because it generally requires very long driving on straightforward highways with full container loads. In addition, the warehouse company generally controls the warehouses where delivery will take place. This means that a transport truck can be loaded and unloaded according to best practices for the self-driving system. Particular highways and roads leading to the warehouses could be designated safe for driverless transport vehicles. Accordingly, a predefined selective driving path will be regulated and approved as safe for precise driverless transport vehicles. In that case, the critical issue will be resolving legal issues. Who is liable, for example, if an accident occurs, the transport company or the vehicle manufacturer? These are long and heavy vehicles that one might think require full human supervision. The autonomous vehicle system will most likely be rented to transport companies by a third-party central-control company.
Autonomous technology could be used for humanoid robot technology at later stages and will be introduced as such by the technology companies in the next few months.
B) Generative AI – Cognitive computing
Generative AI is a pre-trained tool built on supervised and reinforced learning methods nourished by big data. Generative AI is a part of cognitive computing and combines text, numbers, code, images, video, and audio, with an Artificial Intelligence algorithm.
Several new generative AI tools have recently been introduced, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Bard, and Microsoft’s Bing. Generative AI can give humans wisdom powers. The applications of “generative AI” are wide-ranging, revolutionizing consumers, businesses, services, education, and industries.
For generative AI, there are two main revenue streams:
I) Generative AI and the monetized business model.
Ii) Generative AI sold as digital products and services.
Let us use the “Strategic Model of Technology Innovation tool” to understand possible business models and potential revenue and profit scale.
I) Generative AI and the monetized business model
Social media and search engine companies have taken over the advertising vehicle market for a reason. They can offer Merchants real-time insight information to assist consumers in identifying their needs for products and services at the time when they need them. Search engines and social media follow some of the current business models of newspapers, radio, and TV operations. That is, providing free subscriptions and generating revenue through advertising. The business model concept is that the more users and readers there are, the more appealing it is to advertisers through increased advertising reach. This business model is often referred to as the “Monetizing Model.”
The monetizing model is a platform that converts non-revenue user activities into cash flow by bringing revenue-generating activities into play from innovative sources. Social media monetization generates core revenue through sales of user data, advertising, affiliate marketing, premium membership, and other services. Based on each specific business scenario, social media companies exploit various business models, and their models will evolve over time. Generative AI for personal use will compete with search engines and social media platforms. Thus generative AI will make revenue and profit similar to Web browsers (Google and Edge) and social media (Facebook).
II) Generative AI sold as digital products and services
Digital products are sold online and can be retrieved instantly from online devices. Digital products are computer-generated, do not have physical shapes, and are stored in an electronic format, not in a physical warehouse. Digital products are generally sold by downloading an electronic file over the Internet to the consumer’s smartphone, tablet, console, smartwatch, or PC. In some cases, the buyer receives the downloaded content as a file, often stored on a computer or smart device. In that case, the buyer receives audio, video, photography, drawings, designs, art, Web platforms, or text content over the Internet network. Examples of digital products include eBooks and audiobooks, eMusic, videos, computer games and software, and cloud computing software, provided as a service. Furthermore, downloadable online eCourses, training programs, templates, downloadable images, stock photography, and manuals in electronic format. In other cases, digital products, software, and hardware are accessed as cloud services over the Web. Digital products could be both single-item and subscription-based sales.
The following are examples of industries willing to buy generative AI services as digital products:
- Architects and engineers efficiently build simulation models and identify and optimize key design features such as energy efficiency and structural design. With this approach, practicality will be improved while costs are minimized.
- Customer service centers utilize a “chatbot” to resolve all customers’ requests effectively on first contact with minimal contact time. This will improve customer satisfaction at the lowest possible cost. Chatbots are used in verbal communications, generally limited to conversations that resolve specialized tasks and information requests. As the future of technology, chatbots are easy to use, replacing browsing searches, and time-consuming interaction with apps, for example. With continual technological advancements in machine learning algorithms, speech recognition and recommendations will advance to a higher level of accuracy and promptness.
- Software development, creating, testing, and deploying code. In addition to analyzing code, AI can provide suggestions for improvement and identify potential errors before they occur. In this way, AI improves team collaboration, costs, and productivity.
- Healthcare AI technology has tremendous potential for improving medical diagnosis accuracy and reducing diagnostic time. When it was discovered that computer programs might be better than humans at reading X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), mammograms, computed tomography (CT) scans, and ultrasound diagnostics, it opened up a constructive revolution in the healthcare system.
- Translators using AI can get translation suggestions and ideas in any language. AI can do this in real-time; translation into many languages helps people communicate on a massive scale.
- The news and media AI program can uncover news early and write press releases for journalists and news organizations.
- Graphic and creative designers can access AI-generated text, illustrations, images, video content, graphics, and ideas. It enhances their creativity and makes their products more valuable to their customers.
- Perform legal case research by finding relevant papers to your request and summarizing key information from the paper. One can search hundreds of millions of legal cases for research.
The next step to understand the size scale is to evaluate through a time and activity study how much time generative AI can save for each job role.
Understanding how time can be saved using generative AI requires a time and activity study by job role.

Time and activity studies, among other transformation factors, will help us understand how radically generative AI will change each profession.
As shown in the above figure, the customer service center can save 80% of staff time by using a chatbot. This is a significant benefit. Operating an artificial robotic voice customer service center costs only 20% of a traditional customer service center.
On the other hand, architects and engineers can save 20% of staff time. In that case, it is a question if it requires the transformation of the job or if it leads to destroying jobs.
However, for autonomous vehicles in the “established” market, people spend, on average, 0.9 hours driving each day. Public market surveys show they are willing to pay between $5.000 and $10.000 for an autonomous apparatus.
Then as a last step, each market must assess how many customers, industries, or companies will total in that market buy the new technology product and services.
Each industry requires its own study to assess the magnitude of technology innovation. The bottom-up approach using the Strategic Model of Technology Innovation enables us to understand the size and scale of each technology and how it can make revenue and profit. This also includes understanding user relevance and the competition.
Don’t forget to pass this article on to your friends and colleagues.
The book Technology Innovation by Baldur Gudgeirsson is the source of this article.
For reviews of Baldur’s four books, visit: https://www.icebergbooks.com/
